
Constantly dealing with emergency repairs can feel like an uphill battle. This reactive approach to maintenance is expensive, impacting your profits and disrupting your day-to-day operations. Smart businesses are switching to preventive maintenance, a proactive strategy using scheduled routines to keep equipment running smoothly and avoid unexpected breakdowns. This approach minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of your valuable assets, leading to fewer problems, smoother operations, and a healthier bottom line. But how do you transition to this proactive method? The answer lies in a well-structured preventive maintenance schedule template.
A preventive maintenance schedule template forms the backbone of a strong maintenance program. It helps you prioritize essential equipment, allocate resources effectively, and retain valuable institutional knowledge. For example, a template can outline specific maintenance tasks for each piece of equipment, including the frequency of these tasks and the assigned personnel. This provides a clear plan for your team, ensuring that no task is overlooked. Furthermore, a template promotes accountability and consistency, resulting in more effective maintenance procedures.
Implementing a formal preventive maintenance program offers significant advantages. In fact, preventive maintenance (PM) is already a common practice, particularly in manufacturing. As of 2018, roughly 80% of manufacturing plants utilized PM, frequently alongside predictive maintenance. Regular preventive maintenance can cut total maintenance expenses by 12% to 18%, and every dollar invested in PM can save up to five dollars in future expenses. This highlights the substantial return on investment that preventive maintenance delivers. Learn more about maintenance statistics here.
Using a template provides several important benefits:
Reduced Downtime: Addressing potential problems before they become major failures minimizes unexpected equipment breakdowns and the associated downtime.
Cost Savings: Preventing significant breakdowns through routine maintenance is far more economical than expensive emergency repairs and replacements.
Extended Equipment Lifespan: Regular maintenance and prompt repairs help extend the working life of your equipment, maximizing your return on investment.
Improved Safety: A well-maintained workplace is inherently safer. Preventive maintenance reduces the risk of accidents arising from faulty equipment.
Increased Efficiency: A structured maintenance plan optimizes resource use and streamlines work processes, contributing to improved overall efficiency.
Selecting the right template is crucial for success. Think about factors such as your business size, the complexity of your equipment, and your industry’s particular requirements. A basic spreadsheet template might be adequate for smaller businesses, whereas larger organizations may find more advanced software solutions beneficial. Regardless of the format, a well-designed preventive maintenance schedule template allows you to take charge of your maintenance operations and realize significant cost savings and operational enhancements. By shifting from a reactive approach to a proactive one, you lay the groundwork for enduring success.
A well-designed preventive maintenance schedule template is essential for a proactive maintenance strategy. It's the key to shifting from reactive repairs to efficient, scheduled maintenance, saving your business time and money. But what makes a template truly effective? It comes down to understanding the key components that optimize maintenance operations.
A robust template needs specific elements for clarity, accountability, and ease of use. These empower your team to perform tasks effectively and provide data for strategic decisions.
Asset Identification: Clearly identify each asset with a unique ID, description, and location. This prevents confusion and ensures the correct maintenance is performed on the correct equipment.
Task Descriptions: Provide precise descriptions of each task. This ensures technicians understand what needs to be done, regardless of experience. Clear descriptions promote consistency and quality.
Frequency and Schedule: Define the frequency of each task (daily, weekly, monthly, etc.) and create a clear schedule. This ensures timely maintenance and reduces the risk of overlooked tasks. A consistent schedule simplifies resource allocation.
Responsibility Assignment: Assign responsibility for each task to a specific person or team. This promotes accountability and ensures tasks don't get missed. It also streamlines communication.
Record Keeping: Include space for recording details like date completed, technician initials, and notes. This history allows you to track maintenance, identify recurring problems, and improve strategies. For a detailed checklist example, refer to this Office Equipment Maintenance Checklist.
To help understand how these components fit together, let's look at a detailed breakdown in the following table:
Essential Elements of a Preventive Maintenance Template
A comprehensive breakdown of the key components that should be included in any preventive maintenance schedule template
| Template Component | Purpose | Implementation Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Identification | Uniquely identify equipment to avoid confusion | Use a consistent numbering system, detailed descriptions, and precise location information |
| Task Descriptions | Clearly outline maintenance steps | Use action verbs, specific measurements, and clear language to avoid ambiguity |
| Frequency and Schedule | Establish a regular maintenance rhythm | Define clear intervals (daily, weekly, monthly) and assign specific dates or times for tasks |
| Responsibility Assignment | Ensure accountability for each task | Clearly identify individuals or teams responsible and establish communication channels |
| Record Keeping | Track maintenance history and identify trends | Provide dedicated space for recording dates, technician initials, and any relevant observations or notes |
As you can see, each component plays a vital role in the overall success of your preventive maintenance program.
While the core components are essential, additional elements can enhance usability.
Priority Levels: Assigning priority (high, medium, low) helps prioritize tasks based on their importance and impact. This ensures critical tasks are addressed first.
Estimated Time: Including estimated times for each task helps with scheduling and resource allocation. Accurate estimates improve workflow.
Safety Procedures: Incorporate safety precautions for each task. This prioritizes technician safety and reduces workplace accidents.
Cost Tracking: Include fields to track parts, labor, and other expenses. This provides valuable data for budget management.
Consider transitioning from paper templates to digital solutions. Software programs and mobile apps offer automated reminders, real-time updates, and integration with other business systems. This simplifies management and provides insights into operations. This data can inform strategic decisions and improve resource allocation.

By incorporating these elements and adapting them to your needs, your preventive maintenance schedule template becomes a powerful tool for optimizing operations, reducing costs, and extending the life of your equipment.

Generic preventive maintenance schedule templates often miss the mark. Why? Because different industries have unique equipment, regulations, and operational needs. A healthcare facility, for example, has vastly different maintenance requirements compared to a manufacturing plant. Healthcare prioritizes critical, life-saving equipment and strict regulatory compliance. Manufacturing, on the other hand, balances production uptime with necessary maintenance to avoid disruptions.
Commercial property managers face a different set of challenges. They juggle numerous systems, from HVAC and elevators to fire suppression. Their preventive maintenance schedule template needs to cover a broad spectrum of equipment and varying maintenance frequencies. Adapting your template requires a deep understanding of your industry's specific challenges and operational realities.
This means carefully considering the types of equipment used, relevant regulatory requirements, and the potential consequences of downtime. To make your maintenance procedures more efficient and ensure consistency across the board, consider using pre-built operational manual templates.
Start by thinking about the structure of your template. Do you need separate sections for different equipment categories? Should compliance documentation be integrated directly into the template itself? Next, consider maintenance frequencies. Some industries, like healthcare, require more frequent checks on essential equipment.
Others may use usage-based maintenance, triggering tasks after a specific number of operating hours. Creating an effective preventive maintenance schedule template often hinges on optimizing existing resources and using technology wisely. Resource limitations are a significant challenge for many facilities. Nearly 49% of facilities reported this as a major obstacle in 2018.
However, the adoption of Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) has significantly increased, with 52% of industrial plants utilizing these systems by 2021. Your templates need to incorporate these technological advancements and account for resource limitations. More detailed statistics can be found here.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) provide measurable ways to track the effectiveness of your maintenance program. Different industries prioritize different KPIs. A manufacturing plant might focus on Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), while a hospital emphasizes Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) for critical equipment.
Your preventive maintenance schedule template should be designed to collect the data needed to track these vital KPIs. For example, a manufacturing facility might track unplanned downtime hours, while a hospital focuses on the time taken to repair mission-critical equipment.
By tailoring your preventive maintenance schedule template to your specific industry, you go beyond a generic, one-size-fits-all approach. This creates a powerful tool for extending equipment lifespan, minimizing downtime, and achieving operational excellence. It makes sure your maintenance efforts are focused on the most critical needs of your industry.
This targeted approach, combined with effective implementation, empowers your team to proactively manage maintenance and boost overall efficiency. Remember, a well-designed template isn't just a schedule; it's a crucial part of your overall business strategy.
Choosing the right scheduling method for preventive maintenance is crucial for maximizing efficiency. The two primary approaches are time-based and usage-based scheduling. Each has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. This section explores which method works best, and how smart organizations combine them to get the best results.
Time-based scheduling involves performing maintenance at pre-set intervals, like monthly or every six months. This approach is effective for equipment with predictable wear and tear, such as vehicles needing regular oil changes. It simplifies planning and ensures consistent maintenance. It's similar to changing your home's air filter every three months—a regular task based on the calendar.
This approach makes planning straightforward and guarantees consistent upkeep. However, it may lead to unnecessary maintenance if the equipment hasn't been used extensively.
Usage-based scheduling triggers maintenance according to equipment usage, such as operating hours or mileage. This approach is perfect for assets where wear and tear directly correlates with usage, like a delivery truck accumulating mileage. This method can be more efficient than time-based scheduling because maintenance happens only when needed. Think of it like changing your car's oil based on mileage—it ensures the oil change occurs when needed, regardless of driving frequency.
While usage-based scheduling can be more efficient, it requires careful monitoring of equipment usage. This can be challenging for organizations with a large number of assets.
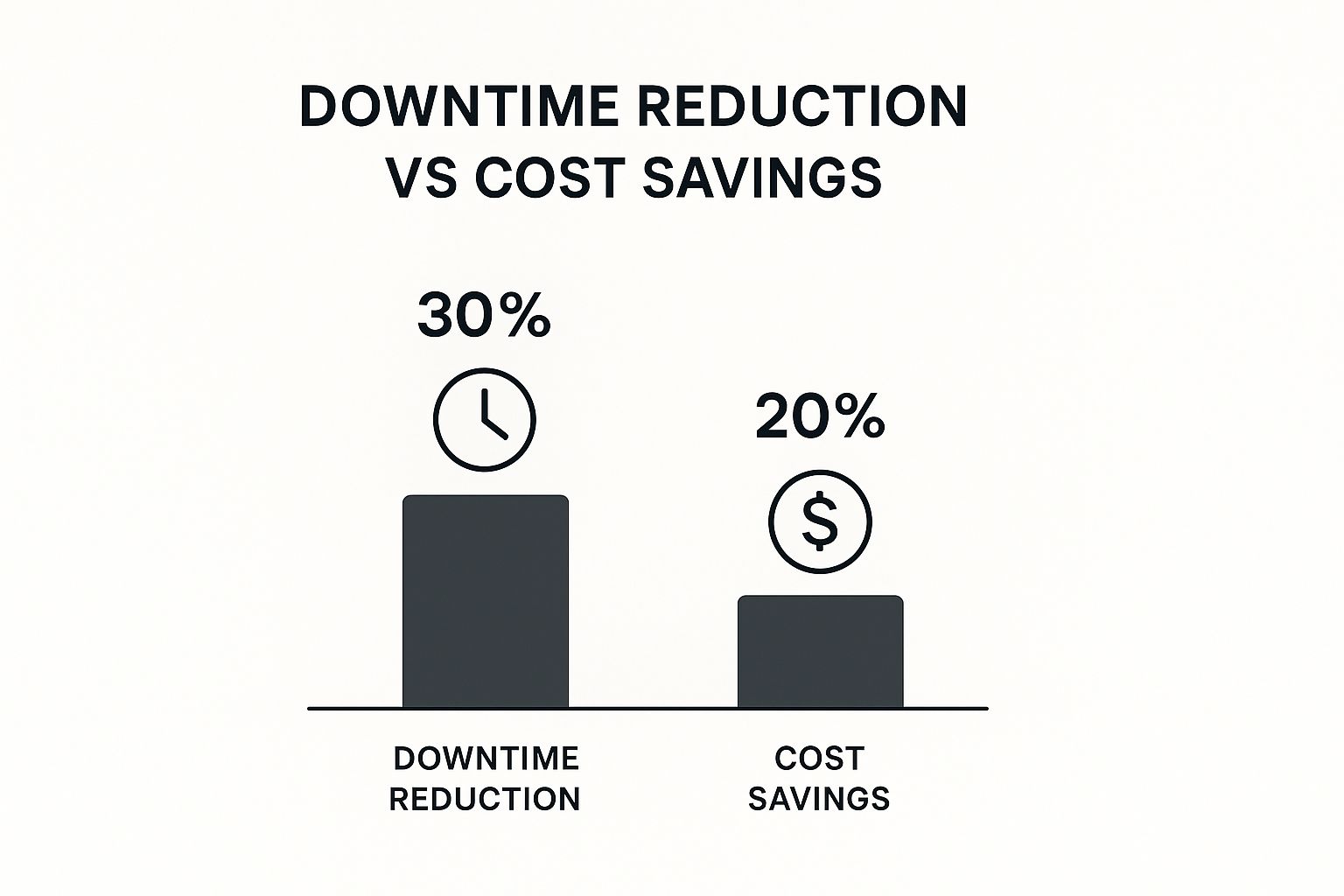
The infographic above illustrates the impact of choosing the right preventive maintenance strategy. A well-structured plan can lead to a 30% reduction in downtime and 20% cost savings. This highlights the importance of selecting the right scheduling method.
Many organizations adopt a hybrid approach, combining time and usage-based scheduling. This allows them to customize their maintenance programs for different assets. A car rental company might change oil based on mileage (usage-based) but rotate tires on a calendar schedule (time-based). This method leverages the strengths of both.
This flexibility makes hybrid approaches suitable for diverse asset types and operational needs. However, it requires more complex planning and tracking compared to single-method approaches.
To help visualize the differences between these methods, consider the following table:
Time-Based vs. Usage-Based Maintenance Scheduling Comparison of different scheduling approaches for preventive maintenance programs
| Scheduling Approach | Best For | Advantages | Limitations | Implementation Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time-Based | Equipment with predictable wear patterns | Simple planning, consistent maintenance | May lead to unnecessary maintenance | Calendar or schedule-based tracking |
| Usage-Based | Assets with usage-dependent wear | Maintenance only when needed, increased efficiency | Requires usage monitoring, can be complex | Meters, sensors, or usage logs |
| Hybrid | Diverse asset types and operational needs | Combines benefits of both, tailored to specific assets | Requires complex planning and tracking | Integrated system for time and usage data |
The table summarizes the key differences between time-based, usage-based, and hybrid maintenance scheduling. Each approach has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice depends on the specific context.
Changing between approaches requires clear communication and training for your team. Explain the why and provide training on the how. Maintain consistent documentation throughout the transition for accurate records.
The ideal approach hinges on your specific needs and equipment characteristics. Consider factors like equipment criticality, failure predictability, downtime costs, and resource availability. Carefully evaluating these factors helps develop a preventive maintenance schedule that optimizes performance and minimizes downtime. At Kwik Kar of Mesquite, we tailor our maintenance recommendations to your vehicle and driving habits, using both time and usage-based approaches. Contact us to learn more about our preventive maintenance services and schedule an appointment.
Remember those bulky paper maintenance schedules? They're becoming a thing of the past. Technology is changing how we handle preventive maintenance, offering software solutions that simplify the whole process. We've come a long way from basic spreadsheets to sophisticated Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS). These systems provide dynamic scheduling, automated workflows, and real-time performance tracking – features unheard of with older methods.
These digital tools allow businesses to ditch static schedules for a proactive, data-driven approach. This means more flexibility and responsiveness, ensuring maintenance happens exactly when needed and minimizing disruptions. It also improves transparency and accountability within maintenance teams.
Switching from simple spreadsheets to powerful CMMS platforms has been a significant improvement for many organizations. Spreadsheets, while helpful for basic tracking, lack the robust features of modern software. CMMS platforms offer a central hub for all maintenance activities, from scheduling and task management to inventory control and reporting.
Think about a manufacturing plant with hundreds of machines. A CMMS can automatically create work orders based on set criteria, like operating hours or calendar dates. This automation eliminates manual data entry, reducing errors and freeing up staff for more important tasks. Plus, these platforms allow for real-time tracking of maintenance, giving valuable insights into equipment performance and maintenance effectiveness.
Mobile access has also changed how field technicians operate. With mobile CMMS apps, technicians can access schedules, get work orders, and update maintenance records right from their phones or tablets. This instant access eliminates delays and improves communication between field teams and managers.
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors takes preventive maintenance even further. IoT sensors monitor equipment conditions in real time, providing data that can predict potential problems. This predictive capability allows for condition-based scheduling, drastically reducing unnecessary maintenance and downtime. This predictive maintenance market is booming. It was valued at $7.85 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach $60.13 billion by 2030, thanks to stricter safety regulations and the growing use of AI. Learn more about these trends here.
Finding the best technology solution depends on your team's size, the complexity of your work, and your budget. Smaller businesses with tighter budgets may find basic software sufficient. Larger companies with more complex needs might require more advanced CMMS platforms with mobile access, IoT integration, and in-depth analytics. At Kwik Kar of Mesquite, we use cutting-edge diagnostic equipment for accurate and efficient maintenance. Contact us to learn more about our preventive maintenance programs.
A well-crafted preventive maintenance schedule template is only as good as its implementation. This section offers a roadmap for turning your template into a successful maintenance program. We'll cover practical strategies to overcome common obstacles, build strong foundations, and cultivate a culture of continuous improvement.
Shifting to a proactive maintenance program can sometimes meet resistance. Obstacles such as limited resources, gaining team buy-in, and juggling competing priorities can be challenging. For instance, securing the budget for new tools or training can be tough. Convincing teams used to reactive maintenance to adopt a new approach requires clear communication and showcasing tangible benefits.
To handle resource constraints, consider starting small. Pilot the program with one team or a specific asset class. Track and measure your successes, then use that data to justify expanding the program. To foster team buy-in, involve technicians in the process from the start. Their insights into the template’s design and implementation will not only increase their acceptance but also uncover practical on-the-ground considerations.
Before rolling out your program, gather crucial asset data. This includes details like equipment specifications, past maintenance history, and performance records. This information will serve as your baseline for measuring program effectiveness. For example, knowing the typical failure rate of a specific machine gives you a benchmark for improvement after implementing the preventive maintenance schedule.
Setting a baseline is crucial for demonstrating Return on Investment (ROI). It provides a comparison point for tracking reductions in downtime, repair expenses, and overall maintenance spending. This concrete data helps demonstrate the program's value and secures ongoing support from stakeholders.
Rolling out a new preventive maintenance schedule requires proper training. Technicians need to understand the template, the updated processes, and why accurate data entry is important. Provide hands-on training covering both the "why" and the "how" behind the program.
A well-trained team ensures consistent execution of the maintenance schedule. This contributes to better data collection, improved equipment performance, and a more efficient maintenance program overall.
To demonstrate the program’s value, choose Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that align with your business goals. Track metrics such as downtime reduction, maintenance cost savings, and Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF).
Calculating the true ROI of preventive maintenance involves comparing implementation costs (training, tools, software) with the achieved savings (fewer repairs, longer equipment lifespan). Presenting this data clearly showcases the program’s value to stakeholders.
A truly successful preventive maintenance program is dynamic, adapting to evolving needs and equipment conditions. Regularly review the program with your team, incorporate feedback from technicians, and adjust schedules as needed.
This feedback loop is essential for continuous improvement. It helps the program stay effective, efficient, and relevant to the organization's operational needs.